What Are the Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Hereditary Angioedema?
Hereditary Angioedema, or HAE, is a rare inherited disorder with episodic swelling of some parts of the body that include the hands, feet, face, and airways. The swelling associated with HAE does not have the usual characteristics of common allergic reactions, which have itching, and it could last for days. Awareness of warning signs, which include abdominal pain, swelling of the face, and tightness in the throat, helps for early diagnosis and management. Untreated, HAE can be fatal with complications, especially if the swelling occurs in the airway. This information enables people to seek early medical care and adopt preventive measures to control the condition better.
What is Hereditary Angioedema?
Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) is an unusual genetic disorder with an inheritance mode. It results from inadequate or dysfunctional production of a protein called C1-inhibitor, which dampens inflammation. This kind of swelling does not respond to such common treatments as antihistamines or steroids for more common types of swelling: allergic reactions. It becomes essential and sometimes challenging to understand how HAE works and manages.
Early Warning Signs of Hereditary Angioedema
Early symptoms of HAE should be recognized before severe complications occur. In most cases, these early warning signs develop gradually, and their severity varies between individuals. The most common indicators are listed below:
- Recurrent Swelling
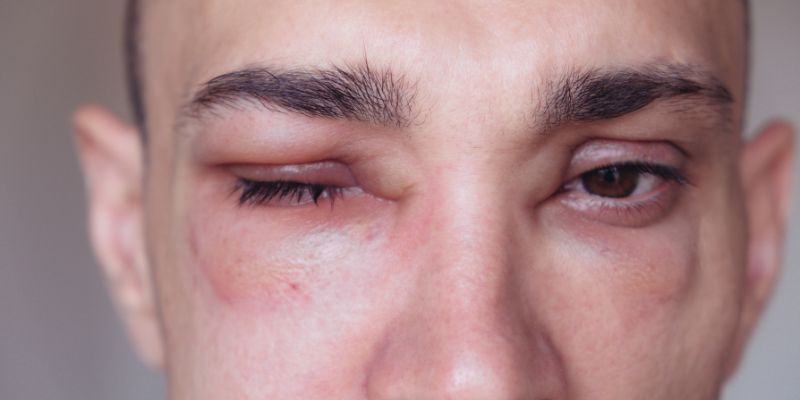
Swelling is the hallmark of HAE and can occur in almost any part of the body, including hands, feet, face. The swelling is usually non-itchy and firm to the touch. It does not create an indentation when pressed and may last several days without treatment. It is not like allergic swelling.
- Abdominal Pain and Discomfort
Abdominal attacks are also a common symptom in HAE patients, which can be confused with other gastrointestinal disorders such as appendicitis. The episodes lead to severe cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In some cases, the pain is so intense that it necessitates emergency medical care.
- Facial Swelling
Swelling of the face may include the lips, eyelids, or cheeks. It is alarming as it develops slowly but very obviously. Although they are not painful, they can be uncomfortable and give a feeling of tightness.
- Throat Tightness or Difficulty Breathing
One of the dangerous symptoms of HAE is swelling in the throat, which might result in breathing difficulty, hoarseness, and eventually suffocation if it's not treated in time. This is a medical emergency requiring prompt attention.
- Skin Rash or Redness (Erythema Marginatum)
This rash is not itchy but may appear as red patches or rings mistaken for an allergic reaction, often occurring before or during an HAE attack and thus may be used as a sign.
Triggers That May Aggravate Symptoms
Knowing what can trigger the worsening of HAE symptoms can prevent the onset of some attacks. Specific triggers are more likely to provoke swelling attacks. By understanding these, patients can adapt their lifestyles and avoid unnecessary risks.
Stress and Anxiety
The occurrence of more frequent and severe HAE attacks could result from stress and anxiety. Psychological stress may arise from problems at work, personal difficulties, or any other source and can alter the body's hormone level to cause an attack. Some people have been advised to engage in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga, to control such problems. Therapy or counseling with physical exercise will help minimize attacks in HAE patients.
Physical Trauma or Surgery
Minor physical trauma, such as cuts or bruises, can cause HAE attacks by inducing an inflammatory reaction in the body. Surgical procedures, dental work, and even strenuous exercise can cause swelling episodes. To avoid such risks, patients should alert their physicians or dentists before any surgical or dental procedures. Doctors may administer prophylactic medications before surgery to minimize the risk of inducing an attack.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes are the most common cause, especially in females. Menstruation, and hormone replacement therapy can exacerbate HAE symptoms. In these periods, hormonal changes in the body can alter the balance of proteins that regulate inflammation. Women with HAE should discuss their condition with their physicians and consider alternative treatments for hormone-based medications when appropriate.

Diagnosis of Hereditary Angioedema
A timely and accurate diagnosis of HAE is necessary for proper disease management. HAE often presents similarly to other diseases like allergic reactions or gastrointestinal diseases; thus, appropriate diagnostic procedures must be performed to avoid misdiagnosis.
- Family History
Since HAE is an inherited condition, a family history of similar symptoms often provides the first clue in diagnosis. The doctor will ask questions about relatives who experience unexplained swelling or abdominal pain. A clear family history of HAE increases the likelihood of a diagnosis and helps narrow down other potential causes of the symptoms.
- Blood Tests
Laboratory tests are key in the diagnosis of HAE. Blood tests measure quantitatively and qualitatively the level and activity of the protein C1-inhibitor. This is either deficient or dysfunctional in patients with HAE. Another diagnostic marker is that the complement level, C4, is ordinarily low during HAE attacks. These tests help distinguish HAE from other conditions that cause a similar swelling.
- Genetic Testing
Genetic testing makes a confirmation diagnosis of HAE possible, as alterations in the SERPING1 gene account for most HAE. Hence, alterations in this gene can result in doctors' diagnosis. Of course, there are families with absolutely no known background of suffering from HAE, meaning the spontaneous mutation is sometimes responsible for this illness. Ensuring accurate diagnoses allows patients to receive appropriate care sooner rather than later.
Conclusion
Hereditary Angioedema is a complex but treatable condition. Early awareness of the manifestations of this condition provides ample opportunities for early diagnosis, leading to successful treatment. Patients need to know the causes of their suffering and must take preventive measures if possible. If you suffer or witness an attack of recurrent swelling and similar symptoms, you would want to consult a medical expert immediately.